The Environmental Impact Of Car Manufacturing – And How It’s Changing

Executive Summary

The automotive industry is a significant contributor to global environmental problems. From resource extraction to manufacturing, use, and disposal, cars leave a substantial carbon footprint. However, significant changes are underway, driven by government regulations, consumer demand, and technological advancements. This article explores the environmental impact of car manufacturing, focusing on the key challenges and the emerging solutions that are reshaping the industry towards a more sustainable future. We will examine the lifecycle of a vehicle, highlighting areas for improvement and celebrating the progress being made in reducing the environmental burden of car production and usage.
Introduction
The hum of a car engine, the sleek lines of a new model – these are images often associated with freedom and progress. But behind the allure of the automobile lies a complex and often troubling reality: the significant environmental impact of car manufacturing and its associated processes. From the mining of raw materials to the eventual disposal of a vehicle, the entire lifecycle contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, pollution, and resource depletion. This article delves into the multifaceted environmental challenges posed by the automotive industry and explores the innovative solutions currently being implemented to mitigate these effects, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable future of transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: What are the biggest environmental impacts of car manufacturing?
A: The biggest impacts include greenhouse gas emissions (primarily CO2) from manufacturing processes and vehicle operation, resource depletion due to the extraction of raw materials (like steel, aluminum, and rare earth elements), water pollution from manufacturing waste, and air pollution from vehicle exhaust and manufacturing emissions.
- Q: Are electric cars truly environmentally friendly?
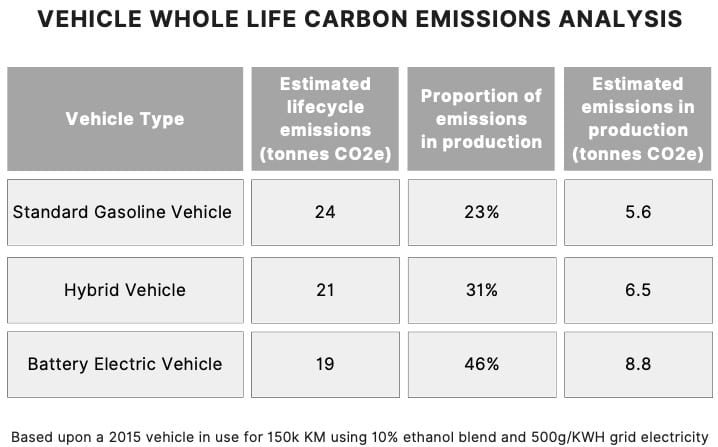
A: While electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, their environmental impact is still complex. The manufacturing process of batteries involves energy-intensive processes and the use of materials with their own environmental footprints. However, the overall lifecycle emissions of electric cars are generally lower than those of gasoline-powered vehicles, and this gap is continually shrinking as battery technology improves and renewable energy sources power the manufacturing process.
- Q: What can I do as a consumer to help reduce the environmental impact of car manufacturing?
A: You can support manufacturers committed to sustainability, choose fuel-efficient or electric vehicles, properly maintain your car to maximize its lifespan, and recycle or responsibly dispose of your vehicle at the end of its life. Advocating for stronger environmental regulations in the automotive industry is also impactful.
Material Sourcing and Extraction
The journey of a car begins long before assembly lines. The extraction of raw materials – iron ore for steel, bauxite for aluminum, various plastics, and rare earth elements for batteries – has devastating environmental consequences. Mining activities lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The transportation of these materials to processing plants adds further to the carbon footprint.
Mining practices: Many mining operations use unsustainable methods, causing significant habitat disruption and pollution. Moving towards responsible mining practices, including reclamation and biodiversity restoration, is crucial.
Transportation of materials: The long-distance transportation of raw materials contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Optimizing logistics and using more sustainable transport modes (e.g., rail instead of road) is essential.
Resource depletion: The car industry consumes vast quantities of finite resources. Circular economy models, promoting the reuse and recycling of materials, are vital to lessen this impact.
Energy consumption in material processing: Processing raw materials into usable components is highly energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuels. Transitioning to renewable energy sources for this stage is paramount.
Waste generation: Mining and material processing generate significant waste, including tailings, slag, and other byproducts, which can cause soil and water contamination. Minimizing waste generation and implementing effective waste management strategies are critical.
Manufacturing Processes
The assembly of a car involves numerous processes, each carrying its own environmental burden. Energy consumption during manufacturing, the use of hazardous chemicals, and the generation of industrial waste all contribute to the overall environmental impact.
Energy consumption: Manufacturing plants often rely on fossil fuels, leading to significant greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency in manufacturing processes are vital steps.
Hazardous chemicals: Many manufacturing processes involve the use of hazardous chemicals that can pollute air and water if not managed properly. Implementing stringent safety protocols and adopting cleaner production methods is essential.
Waste generation: Car manufacturing generates substantial waste, including scraps of metal, plastic, and other materials. Waste reduction strategies, such as improved design for disassembly and recycling programs, are crucial.
Water usage: Manufacturing processes require significant amounts of water. Implementing water-efficient technologies and recycling water are essential for reducing the environmental impact.
Air pollution: Manufacturing processes can release various air pollutants, contributing to respiratory problems and climate change. Investing in cleaner technologies and implementing stricter emission controls are necessary.
Vehicle Use and Operation
Once a car is on the road, its environmental impact continues. Fuel consumption, exhaust emissions, and the generation of traffic congestion all contribute to various environmental problems.
Greenhouse gas emissions: The combustion of fossil fuels in gasoline and diesel vehicles releases substantial amounts of greenhouse gases, particularly CO2, contributing significantly to climate change. Electric vehicles and alternative fuels offer a solution to this problem.
Air pollution: Exhaust emissions contain various pollutants, including particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which can have severe health and environmental consequences. Stricter emission standards and the adoption of cleaner technologies are needed.
Noise pollution: Vehicle noise can negatively impact human health and wildlife. Quieter vehicle designs and effective noise barriers can mitigate this impact.
Traffic congestion: Congestion leads to increased fuel consumption, emissions, and wasted time. Investing in public transportation, promoting cycling and walking, and implementing smart traffic management systems are crucial.
Road infrastructure impacts: The construction and maintenance of roads have environmental impacts, including habitat loss, material consumption, and emissions from construction activities. Sustainable road design and construction practices are necessary.
End-of-Life Vehicle Management
At the end of its lifespan, a car becomes a source of waste. Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination and resource loss.
Recycling and reuse: Recycling vehicle components reduces the need for new materials and conserves resources. Improving recycling technologies and implementing effective recycling programs are crucial.
Waste management: Proper disposal of hazardous materials, such as batteries and fluids, is essential to prevent environmental contamination. Implementing strict regulations and developing efficient waste management systems are necessary.
Landfill avoidance: Sending vehicles to landfills contributes to land degradation and pollution. Promoting recycling and reuse significantly reduces landfill burden.
Circular economy models: Designing vehicles for disassembly and recycling from the outset facilitates efficient resource recovery and waste reduction.
Extended producer responsibility: Holding manufacturers accountable for the end-of-life management of their vehicles incentivizes them to design more sustainable vehicles and invest in recycling infrastructure.
Technological Advancements and Sustainable Solutions
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and growing environmental awareness.
Electric vehicles (EVs): EVs offer a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, although their manufacturing processes require careful consideration of environmental impacts.
Hybrid vehicles: Hybrids combine internal combustion engines with electric motors, offering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Alternative fuels: Biofuels and hydrogen fuel cells represent potential alternatives to gasoline and diesel, but their sustainability needs thorough evaluation.
Lightweight materials: Using lighter materials in car manufacturing reduces fuel consumption and emissions.
Improved manufacturing processes: Adopting more efficient and cleaner production methods reduces energy consumption and waste generation.
Conclusion
The environmental impact of car manufacturing is undeniable, but it is not insurmountable. The automotive industry is undergoing a rapid transformation towards greater sustainability. By embracing innovative technologies, promoting responsible sourcing and manufacturing practices, and implementing effective end-of-life vehicle management, we can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of automobiles. The shift towards electric vehicles, coupled with improvements in battery technology and renewable energy sources, holds immense promise for a greener future of transportation. The journey towards a truly sustainable automotive industry requires collaborative efforts from manufacturers, governments, consumers, and researchers – working together to create a future where mobility and environmental stewardship coexist harmoniously.
Keyword Tags
- Car Manufacturing
- Environmental Impact
- Sustainability
- Electric Vehicles
- Green Technology